Since this page contains information from nearly all other pages, this will remain under active construction until all notes have been fully updated.
#
Glossary*
#
A
Access control is restricting access to resources.
Access management is the process of managing access to resources.
Grouping of resources.
An agreed-upon procedure is a standard a company or client outlines when it hires an external party to perform an audit on a specific test or business process. The procedures, which are called audit standards, are designed and agreed upon by the entity conducting the audit, as well as any appropriate third parties.
The auditor does not provide an opinion; rather, the entities or third parties form their own conclusions based on the report.
Solely cognitive-based, focusing on a system-s ability to analyze past data and make future decisions.
The annualized loss expectancy is a product of the yearly estimate for the exploit (ARO) and the loss in value of an asset after an SLE.
ALE = SLE * ARO
Separation of resources.
Apache CloudStack creates, manages, and deploys clouds. It is an open-source application. It is software utilized to deploy and manage large networks of virtual machines, that need to be highly available.
It is deployed as a highly scalable IaaS computing platform.
An API gateway translates requests from clients into multiple requests to many microservices and delivers the content as a whole via an API it assigns to that client/session.
API gateways can provide access control, rate limiting, logging, metrics, and security filtering services.
Determines the legal standing of a case or issue.
The application has been approved by management.
The application meets technical requirements.
Artificial intelligence is the ability of devices to perform human-like analysis. Artificial intelligence operates by consuming a large amount of data and recognizing patterns and trends in the data.
Contains humanized and analytical types.
Anything of value to a company.
Attributes are facets of an identity. Attributes can be relatively static (like an organizational unit) or highly dynamic (IP address, device being used, if the user authenticated with MFA, location, etc.).
Auditability is collecting and making available necessary evidence related to the operation and use of the cloud.
Authentication is the process of confirming an identity. When you log in to a system you present a username (the identifier) and password (an attribute we refer to as an authentication factor).
Authentication is often referred to as AuthN.
An authoritative source is the root source of an identity, such as the directory server that manages employee identities.
Authorization is the process of granting an identity access to something (.e.g. data or a function).
Authorization is often referred to as AuthZ.
#
B
A bastion host is a method for remote access to a secure environment. The bastion host is an extremely hardened device that is typically focused on providing access to one application or for one particular usage. Having the device set up in this focused manner makes hardening it more effective. Bastion hosts are made publicly available on the Internet.
The difference between a jump server and a bastion host is that a jump server is intended to breach the gap between two security zones and have a gateway to obtain access to something inside of the other security zone. A bastion host is outside of your security zone and will require additional security considerations.
Testing the program as it functions, in runtime.
Business continuity efforts are concerned with maintaining (or "continuing") critical operations during any interruption in service.
Business continuity is defined as the capability of the organization to "continue" delivery of products or services at acceptable predefined levels following a disruptive incident. It focuses primarily on the continuity of business processes (as opposed to technical processes).
Business continuity management is the process by which risks and threats are actively reviewed and managed at set intervals as part of the overall risk management process.
BCM is defined as a holistic management process that identifies potential threats to an organization and the impacts to business operations those threats, if realized, might cause.
It provides a framework for building organizational resilience with the capability of an effective response that safeguards the interests of its key stakeholders, reputation, brand, and value-creating activities.
The business continuity plan allows a business to plan what it needs to do to ensure that its key products and services continue to be delivered in case of a disaster.
Business continuity plans typically outline how to maintain or "continue" business operations back to the point of permanent operations. It allows an enterprise to plan what is necessary to ensure that its key products and services will "continue" to be available in the event of a disaster, and that disruption to the business is minimized as much as possible.
The BCP is not critical to the continuation of services in the event of a business interruption. BC, however, is. The BCP is drafted to support BC.
A business requirement is an operational driver for decision making and input for risk management.
Business rules are lists of statements that tell you whether you may or may not do anything or that give you the criteria and conditions for making a decision.
#
C
A way of determining a target's maturity in terms of process documentation and repeatability. Contains five levels. Is typically not associated with security, however.
Capacity is the measurement of the degree to which the cloud can support or provide service.
A design methodology in which a datacenter arranges racks within long rectangles with a long side facing the wind to provide natural cooling.
Typically a third-party entity or company that looks to extend or enhance value to multiple customers of cloud-based services through relationships with multiple cloud service providers. It acts as a liaison between cloud services customers and cloud service providers, selecting the best provider for each customer and monitoring the services.
A third-party entity offering independent identity and access management (IAM) and key management services to CSPs and cloud customers, often as an intermediary. This can take the form of a variety of services, including SSO, certificate management, and cryptographic key escrow.
?
A cloud application is a software application accessed via the internet and which may include an agent or applet installed locally on the user's device.
Responsible for adapting, porting, or deploying an application to a target cloud environment.
The cloud application architect is responsible for prepping and deploying an application to the cloud environment. This person will work alongside development and implementation resources to ensure that the performance, reliability, and security of an application are sustained over the lifecycle of the application. Knowledge and application of the phases of the SLDC, including assessment, verification, and testing are required.
CAMP is a specification geared towards PaaS. The specification indicates that for consumers this will provider for "portability between clouds." This is accomplished by standardization of the management API, which allows use cases for deploying, stopping, starting, and updating applications.
A pitfall in which application development in cloud environments is much different since applications are built on web service frameworks and typically do not support legacy systems and programming languages.
Responsible for an organization's cloud computing strategy.
- Responsibilities include determining when and how a private cloud meets the policies and needs of an organization's strategic goals.
- Architecting the private cloud, designing/deploying hybrid cloud solutions.
- Understand and evaluate technologies, vendors, services, to support private and hybrid clouds.
The cloud architect is responsible for an organization's cloud computing strategy. Part of the responsibilities include determining when and how a private cloud meets the policies and needs of an organization's strategic goals. Further, responsibilities include:
- Architecting the private cloud
- Designing/deploying hybrid cloud solutions
The architect has a key role in understanding and evaluating technologies, vendors, services, to support private and hybrid cloud. The architect will be required to build relationships between customers and team members.
Augmenting internal, private datacenter capabilities with managed services during times of increased demand.
The organization might have datacenter assets it owns, but it can't handle the increased demand during times of elevated need (crisis situations, heavy holiday shopping periods, and so on), so it rents the additional capacity as needed from an external cloud provider.
The cloud carrier is the intermediary that provides connectivity and transport of cloud services between the CSPs and the cloud service consumers.
The intermediary that provides connectivity and transport of cloud services between the CSPs and the cloud service consumers.
The application of scientific principles, technological practices, and derived and proven methods to reconstruct past cloud computing events through identification, collection, preservation, examination, interpretation, and reporting of digital evidence.
Ensures the various storage types and mechanisms utilized within the cloud environment meet and conform to the relevant SLAs and that the storage components are functioning according to their specified requirements.
A cloud architect that focuses on storage. A focal point is to make sure storage types and mechanisms used in the cloud environment meet requirements and the relevant SLAs and that the storage components function according to their specifications.
Deals with which type of cloud you will be leveraging: private, public, community, or hybrid.
Full stack engineering, automation and development of the infrastructure are key aspects of the role. Interactions with cloud administrators and security practitioners will be required for debugging, code reviews, and security assessment requirements.
Cloud migration is the process of transitioning all or part of a company's data, applications, and services from onsite premises to the cloud, where the information can be provided over the Internet on an on-demand basis. The steps in a cloud migration include:
- Choosing a provider
- Planning
- Migrating
- Testing and validation
- Maintaining
Concerned with the actual movement of the data, application, and services to the cloud.
A term used to describe the deployment of a company's cloud computing strategy, which typically first involves selecting which applications and services will reside in the public cloud and which will remain on-site behind the firewall or in the private cloud.
A cloud service auditor can provide value by determining the effectiveness of the CSP, identify control deficiencies within the consumer organization, and provide an assessment of the quality of service. This would include determining if the SLA is being met.
Third-party organization that verifies attainment of SLAs.
A third party that looks to add value to customers of cloud-based services working with multiple CSPs. Value can come from activities such as customizing the services or monitoring the services.
A third-party entity which acts as a liaison between customers and CSPs ideally selecting the best provider for each customer. The CSB acts as a middleman to broker the best deal and customize services.
Anyone who is purchasing a cloud service. This could be an individual or an organization.
Individual or entity that utilizes or subscribes to cloud-based services or resources.
Someone who connects (or integrates) existing systems and services to the cloud for a cloud customer.
Responsible for policy design, business agreement, pricing models, and SLAs. This role interacts with cloud management and customers. In addition, the role will work with the cloud administrator to implement SLAs and policies.
A role within a CSP that provides audit data when requested or required, manages inventory and assets, prepares systems for the cloud, and manages and maintains services.
The service provider sets the governance.
A service provider that offers customer storage or software solution available via a public network, usually the Internet. The cloud provider dictates both the technology and operational procedures involved.
The CSP will own the datacenter, employ the staff, own and manage the resources (hardware and software), monitor service provision and security, and provide administrative assistance for the customer and the customer's data and processing needs.
Examples include Amazon Web Services, Rackspace, and Microsoft Azure.
The cloud service user has the legal responsibility for data processing that is carried out by the CSP.
The cloud service user is also known as the data controller.
The Cloud Standards Customer Council (CSCC) is an end-user advocacy group. It is dedicated to accelerating cloud's successful adoption, as well as to drilling down into the standards, security, and interoperability issues that surround the transition to the cloud.
Focuses on user groups and the mapping, segregations, bandwidth, and reliability of storage volumes assigned. Additionally, this role may work with network and cloud administrators to ensure SLAs are met.
Cloud testing is load and performance testing conducted on the cloud applications and services, to ensure optimal performance and scalability under a wide variety of conditions.
Someone using cloud services. It could be an employee of a company who is a cloud customer or just a private individual.
Not all cloud users are staff of cloud customers. Many cloud users are simply individuals who are using publicly available cloud services for their personal purposes, such as a person who has a OneDrive account to sync their data.
The act of adding the name "cloud" to a non-cloud service and selling it as a cloud solution.
The process of isolating intake air into a single aisle for two separate rows of server cages.
In this configuration, racks are configured such that the fronts of the devices face each other.
The existing set of rulings and decisions made by courts, informed by cultural mores and legislation. These create precedents, which each party will cite in court as a means to sway the court to their own side of a case.
Includes a variety of compliance services such as data encryption, disaster recovery, reporting, and vulnerability scanning.
A cloud server's compute parameters depend on the number of CPUs and the amount of RAM used. The ability to allocate these resources is a vital compute concern.
Protecting information from unauthorized access/dissemination.
Configuration items can be applied to anything designated for the application of the elements of configuration management and treated as a single entity in the configuration-management system. Examples of CI types include:
- Hardware/Devices
- Software/Applications
- Communications/Networks
- Location
- Database
- Service
- Documentation
- People (Staff and Contractors)
A self-assessment performed by cloud providers, detailing their evaluation of the practice areas and control groups they use in providing their services.
Includes the tools and processes to identify sensitive information in storage.
Act as mechanisms designed to restrict a list of possible actions to allowed or permitted actions. If a control is breached, the next step of mitigating is a countermeasure. Proactive.
A cost-benefit analysis (CBA) is the process used to measure the benefits of a decision or taking action minus the costs associated with taking that action. It determines whether certain activities (such as BC/DR) are worth implementing. The CBA will compare the costs of a disaster and the impact of downtime against the cost of implementing the BCDR solution. Another example would be whether the movement to a cloud model would be lower than the cost of not moving to the cloud.
Countermeasures are what is deployed once a control has been breached. Reactive.
The CIP (Critical Infrastructure Plan), developed by NERC (North American Electric Reliability Corporation), is a set of requirements designed to secure the assets required for operating North America's bulk electric system.
Cross-cutting aspects are behaviors or capabilities which need to be coordinated across roles and implemented consistently in a cloud computing system.
An example of a cross-cutting aspect is security.
Often used to prove liability.
#
D
The person who either alone or jointly with other persons determines the purposes for which and the manner in which any personal data is processed; this entity determines the "why" and "how" personal data is processed.
In the cloud context, the data controller is usually the cloud customer. From an international perspective, the data controller is also known as the data owner.
Data custodians are responsible for the safe custody, transport, data storage, and implementation of business rules. This is any organization or person who manipulates, stores, or moves the data on behalf of the data owner.
The custodian is usually a specific entity in charge of maintaining and securing the privacy-related data on a daily basis, as an element of the data's use; for example, this could be a database administrator hired by the CSP.
The data custodian must adhere to any policies set forth by the data owner in regard to the use of the data.
In the cloud context, the data custodian is usually the cloud service provider. From an international perspective, the data custodian is also known as the data processor.
The entity that holds the legal rights and control over a set of data. Data owners define distribution and associated policies.
In most cases, this is the organization that has collected or created the data. This is also the individual with rights and responsibilities for that data; this is usually the department head or business unit manager for the office that has created or collected a certain dataset.
In the cloud context, the data owner is usually the cloud customer. From an international perspective, the data owner is also known as the data controller.
Any person other than the data owner who processes the data on behalf of the data owner/controller.
In the cloud context, the data processor is usually the cloud service provider. From an international perspective, the data processor is also known as the data custodian.
Any data left over after sanitization and disposal methods have been attempted.
The process of copying data from one location to another. The system works to keep up-to-date copies of its data in the event of a disaster.
Involves an outside company providing advanced analytics applications (gathered using data science) to corporate clients for their business use.
The person responsible for data content, context, and associated business rules.
While the data owner maintains sole responsibility for the data and the controls surrounding that data, there is sometimes the additional role of data steward, who will oversee data access requests and the utilization of the data.
The individual who is the focus of personal data.
Captures and records, at a minimum, all SQL activity in real time or near real time, including database administrator activity, across multiple database platforms; and can generate alerts on policy violations.
A DAM operates at layer 7 of the OSI model.
Can we meet our demand requirements (can we scale up and down)? Elasticity in the cloud solves this.
The Diffie-Hellman key exchange process is used for asymmetric encryption and is designed to allow two parties to create a shared secret (symmetric key) over an untrusted medium.
Diffie-Hellman is not a symmetric algorithm; it is an asymmetric algorithm used to establish a shared secret for a symmetric key algorithm.
Digital forensics is generally considered the application of science to the identification, collection, examination, and analysis of data while preserving the integrity of the information and maintaining a strict chain of custody for the data.
Uses the senders private key and a hash to guarantee the integrity and the origin (authenticity/non-repudiation) of a message. This method requires a PKI.
Disaster recovery efforts are focused on the resumption of operations after an interruption due to disaster.
Disaster recovery is a subset of business continuity. It is the process of saving data with the sole purpose of being able to recover it in the event of a disaster. Disaster recovery includes backing up systems and IT contingency plans for critical functions and applications.
Disaster recovery focuses on technology and data policies (as opposed to business processes).
The disaster recovery plan allows a business to plan what needs to be done immediately after a disaster to recover from the event.
Disaster recovery planning is the process by which suitable plans and measures are taken to ensure that, in the event of a disaster, the business can respond appropriately with the view to recovering critical and essential operations to a state of partial or full level of service in as little time as possible.
DRP is usually part of the BCP and typically tends to be more technical in nature. Addresses what needs to be accomplished during a disaster to restore business processes in order to recover from the event.
A company practices due care by developing (taking action) security policies, procedures, and standards. Due care shows that a company has taken responsibility for the activities that take place within the corporation and has taken the necessary steps to help protect the company, its resources, and employees from possible risks.
Due care is the duty owed by one entity to another, in terms of a reasonable expectation.
Due care is the minimal level of effort necessary to perform your duty to others; in cloud security, that is often the care that the cloud customer is required to demonstrate in order to protect the data it owns.
The lack of due care is often considered negligence.
Due diligence is understanding (researching) the current threats and due care is implementing countermeasures (taking action) to provide protection from those threats.
Due diligence is the act of investigating and understanding the risks the company faces.
Due diligence is the legal concept that describes the actions and processes a cloud customer uses to ensure that a reasonable level of protection is applied to the data in their control.
Due diligence requires that an organization continually scrutinize their own practices to ensure they are always meeting or exceeding requirements for protection of assets and stakeholders.
Due diligence is any activity taken in support or furtherance of due care.
Due diligence is understanding (researching) the current threats and due care is implementing countermeasures (taking action) to provide protection from those threats.
The process in which cloud environments are constantly monitored and maintained to ensure that the resources are available when needed and that nodes share the load equally so that one node doesn't become overloaded.
#
E
Are we doing the right things properly and are we getting the benefits? Are we going about it in the most efficient manner to achieve the most benefits?
The flexibility of allocating resources as needed for immediate usage, instead of purchasing resources according to other variables.
Applications or software that a business would use to assist the organization in solving enterprise problems.
Adds essential features such as archiving and disaster recovery to cloud backup solutions.
ERM includes managing overall risk for the organization, aligned to the organization's governance and risk tolerance. Enterprise risk management includes all areas of risk, not merely those concerned with technology. It is the overall management of risk for an organization.
An entitlement maps an identity (including roles, personas, and attributes) to an authorization. The entitlement is what they are allowed to do, and for documentation purposes we keep these in an entitlement matrix.
The person or "thing" that will have an identity. It could be an individual, a system, a device, or application code.
Eucalyptus is a paid and open-source computer software building AWS-compatible private and hybrid cloud computing environments.
The European Economic Area, abbreviated as EEA, consists of the Member States of the European Union (EU) and three countries of the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) (Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway; excluding Switzerland). The Agreement on the EEA entered into force on 1 January 1994.
According to the ITIL framework, an event is defined as a change of state that has significance for the management of an IT service or other CI. This could be any unscheduled adverse impact to the operating environment.
Events are anything that occur in the IT framework. As a result, the term can also be used to mean an alert or notification created by an IT service, CI, or monitoring tool.
Events often require IT operations staff to take actions and lead to incidents being logged.
Not all events are incidents, but all incidents are events.
An event is distinguished form a disaster by the duration of impact. We consider events impact to last 3 days or less.
Automates detection and remediation of security issues.
An instance of compromise.
#
F
Fault tolerance involves the use of specialized hardware that can detect faults and automatically switch to redundant components or systems.
Should be used when the goal is to eliminate system downtime as a threat to system availability altogether.
Federated SSO is typically used for facilitating interorganizational and intersecurity domain access to resources leveraging federated identity management.
An association of organizations that come together to exchange information as appropriate about their users and resources to enable collaborations and transactions.
FAM monitors and records all activity within designated file repositories at the user level, and generate alerts on policy violations.
Do we have the funds and can we allocate them appropriately? Are we receiving a good return on investment (ROI)? Are we good stewards of the money entrusted to us? Are we making a profit?
Forensic science is generally defined as the application of science to the law.
The idea of moving an existing legacy enterprise application to the cloud with little or no code changes.
A variation to the Smurf attack is the Fraggle attack. The attack is essentially the same as the Smurf attack but instead of sending an ICMP echo request to the direct broadcast address, it sends UDP packets.
Functional testing is performed to confirm the functional aspect of a product. It verifies that a product is performing as expected based on the initial requirements laid out.
Used to duplicate processing capability at a secondary location. The secondary location could be with the same CSP or it could be a different CSP. It occurs anytime a needed function, including DNS, database, or other functionality is replicated to a CSP's other facilities.
#
G
To create an accurate frame of reference, a gap analysis is conducted. This is like a lightweight audit in that there are generally findings of weaknesses or vulnerabilities, but the purpose is to identify those weaknesses so they can be remediated prior to any actual audit work. It also provides a starting point for those organizations in the early stages of an information system program development, providing them with a clear starting point.
Gap analysis benchmarks and identifies relevant gaps against specified frameworks or standards. This includes reviewing the organization's current position/performance as revealed by an audit against a given standard.
The value of such an assessment is often determined based on what you did not know or for an independent resource to communicate to relevant management or senior personnel such risks, as opposed to internal resources saying what you need or should be doing.
Typically, resources or personnel who are not engaged or functioning within the area of scope perform gap analysis. The use of independent or impartial resources is best served to ensure there are no conflicts or favoritism. Perspectives gained from people outside the audit target are invaluable because they may see possibilities and opportunities revealed by the audit, whereas the personnel in the target department may be constrained by habit and tradition.
GAAP is a combination of authoritative standards (set by policy boards) and the commonly accepted ways of recording and reporting accounting information. GAAP aims to improve the clarity, consistency, and comparability of the communication of financial information.
These are the industry standards, also recognized by the courts and regulators, that accountants and auditors must adhere to in professional practice. Many of these deal with elements of the CIA Triad, but they also include aspects such as conflict of interest, client privacy, and so forth.
A standard framework of guidelines for financial accounting.
A geofence is a virtual perimeter for a real-world geographic area.
#
H
A device that can safely store and manage encryption keys used in servers, data transmission, log files, and so forth.
The key difference between HSM and TPM is that an HSM manages keys for several devices, whereas a TPM is specific to a single device.
Able to detect corruption.
High availability makes use of shared and pooled resources to maintain a high level of availability and minimize downtime. It typically includes the following capabilities:
- Live recovery
- Automatic migration
Should be used when the goal is to minimize the impact of system downtime.
Intended to allow for processing of encrypted material without decrypting it first. Since the data is never decrypted, the provider and anyone trying to intercept communication between the user and the cloud would never have the opportunity to view the data in plaintext form.
Grouping multiple honeypot systems to form a network that is used in the same manner as the honeypot, but with more scalability and functionality.
Honeypots are computer systems setup to look like production systems using the modern concept of deception. They contain an operating system and can mimic many common systems such as Apache or IIS web servers, Windows file shares, or Cisco routers. A honeypot could be deployed with a known vulnerability that an attacker would be enticed to exploit. While it appears vulnerable to attack, it is in fact protection the real systems from attack while gathering defensive information such as the attacker's identity, access, and compromise methods.
Used to detect, deflect, or in some manner counteract attempts at unauthorized use of information systems.
Enticement vs. entrapment. The real term to be used should be "distract".
The process of isolating exhaust heat into a single aisle for two separate rows of server cages.
In this configuration, racks are configured such that the backs of the devices face each other.
Incorporates emotional intelligence, cognitive learning and responses, and also expands to include social intelligence.
#
I
The means by which an identity can be asserted. For digital identities this is often a cryptological token. In the real world it might be your passport.
The unique expression of an entity within a given namespace. An entity can have multiple digital identities, such as a single individual having a work identity (or even multiple identities, depending on the systems), a social media identity, and a personal identity. For example, if you are a single entry in a single directory server then that is your identity.
According to the ITIL framework, an incident is defined as an unplanned interruption to an IT service or a reduction in the quality of an IT service.
Essentially, incidents are unscheduled events.
Not all events are incidents, but all incidents are events.
An attack technique that derives sensitive material from an aggregation of innocuous data.
The activities that are performed by an organization to design, plan, deliver, operate and control IT services offered to customers.
ITSM makes it possible to:
- Ensure portfolio management, demand management, and financial management are all working together for efficient service delivery to customers and effective charging for services if appropriate
- Involve all the people and systems necessary to create alignment and ultimately success
A type of IT setup wherein developers or operations teams automatically manage and provision the technology stack for an application through software, rather than using a manual process to configure discrete hardware devices and operating systems.
The process of ensuring that data is real, accurate, and protected from unauthorized modification.
An ISA is an individual who has earned a certificate from the PCI Security Standards Company for their sponsoring organization. This certified person has the ability to perform PCI self-assessments for their organization.
IPsec is a framework for providing secure transmission of sensitive information over unsecured networks such as the Internet. IPSec works at the network layer, protecting and authenticating IP packets between participating IPsec endpoints.
IPsec can provide the following network security services:
- Confidentiality by encrypting packets before sending them across a network.
- Integrity by authenticating packets sent to ensure that the data has not been altered during transmission.
- Authentication of the source of the IPsec packets sent.
- Antireplay by detected and rejected replayed packets.
Downsides to IPsec:
- IPsec adds overhead to network traffic
- Not NAT friendly
IPsec does not always tunnel traffic. GRE is a technology leveraged by IPsec that performs tunneling. IKE is another aspect of IPsec that provides encryption.
#
J
A jump server, jump host or jump box is a system on a network used to access and manage devices in a separate security zone. A jump server is a hardened and monitored device that spans two dissimilar security zones and provides a controlled means of access between them. The most common example is managing a host in a DMZ from trusted networks or computers.
The difference between a jump server and a bastion host is that a jump server is intended to breach the gap between two security zones and have a gateway to obtain access to something inside of the other security zone. A bastion host is outside of your security zone and will require additional security considerations.
This usually determines the ability of a national court to decide a case or enforce a judgment or order.
#
K
A known error is an identified root cause of a problem.
#
L
A LOI outlines the general plans of an agreement between two or more parties before a legal agreement is finalized.
The measure of responsibility an entity has for providing due care. An organization can share risk, but it cannot share liability.
A limit creates a maximum ceiling for a resource allocation.
The risk that the client cedes control to the cloud provider.
#
M
Enables an organization to know all of the locations where data is present within an application and within other storage. Allows for the ability to implement security controls and policies by understanding what type of data is present in the system.
The difference between using a CSP and an MSP is that when using an MSP, the cloud customer has full control over governance.
Distinguishing characteristics of MSPs include:
- Network Operations Center (NOC)
- Help Desk
- Remote Monitoring
- Proactive Maintenance
- Predictive Billing
A measure of how long it would take for an interruption in service to kill an organization. For example, if a company would fail because it had to halt operations for a week, then it's MAD is one week.
MAD is measured in time.
See
See
A nonbinding agreement between two or more parties outlining the terms and details of an understanding, including each parties' requirements and responsibilities.
Microsoft Deployment Toolkit is a computer program that permits network deployment of Microsoft Windows and Microsoft Office.
A term used to describe software that works between an operating system and another application or database of some sort. Typically operates above the transport layer and below the application layer.
Multitenancy refers to the notion of hosting multiple cloud tenants on a single host while sharing resources.
#
N
The NFPA publishes standards regarding fire protection.
Natural disasters are a category of risks to cloud deployments that is based solely on geography and location. Regulatory violations are not always based on location. They can also be based on the type of industry.
Network forensics is defined as the capture, storage, and analysis of network events. The idea is to capture every packet of network traffic and make it available in a single searchable database so that the traffic can be examined and analyzed in detail.
Includes network services from third-parties to customers that do not want to build their own networking infrastructure.
The assurance that a specific author actually did create and send a specific item to a specific recipient and that it was successfully received. The sender of the message cannot later credibly deny having sent the message, nor can the recipient credibly claim not to have received it.
#
O
Outage duration is the length of time of a documented outage and is expressed as an amount of time (minutes, hours, days).
Dependency-Check is a Software Composition Analysis (SCA) tool that attempts to detect publicly disclosed vulnerabilities contained within a project's dependencies. It does this by determining if there is a Common Platform Enumeration (CPE) identifier for a given dependency. If found, it will generate a report linking to the associated CVE entries.
A utility that identifies project dependencies and checks whether there are any known, publicly disclosed, vulnerabilities.
#
P
The expression of an identity with attributes that indicates context. For example, a developer who logs into work and then connects to a cloud environment as a developer on a particular project. The identity is still the individual, and the persona is the individual in the context of that project.
Any information relating to an identified or identifiable natural personal data subject; an identifiable person is one who can be identified, directly or indirectly, in particular by reference to an identification number or to one or more factors specific to his or her physical, physiological, mental, economic, cultural, or social identity.
Access decisions can be enforced at various points with various technologies.
Establishes the security and access policies based on business needs and the degree of acceptable risk.
A portfolio consists of all endeavors undertaken by an organization. We are looking to show value for each individual endeavor but also the IT program as a whole. For example, are we receiving the value from cloud services that we're looking for?
The protection of PII.
A problem is the unknown root cause of one or more incidents, often identified as a result of multiple similar incidents.
Processing is any manipulation of the data, to include security or destroying it, in electronic or hard-copy form. Viewing data is not considered processing.
Based on a judge's discretion, can we demonstrate we've acted responsibly as a prudent person would? What type of action would a prudent person exercise in a particular situation?
#
Q
QSAs are the independent groups/entities which have been certified by PCI SSC for compliance confirmation in organization procedures.
A theoretical technology which allows superposition of physical states to increase both computing capacity and encryption keyspace.
#
R
A data structure or collection of information that is retained by an organization for legal, regulator, or business reasons.
The RPO indicates the amount of acceptable data loss measured in terms of how much data can be lost before the business is too adversely affected.
The point in time at which you would like to restore to. For instance, if an organization performs daily full backups and the BCDR plan includes a goal of resuming critical operations using the last full backup, the RPO would be 24 hours.
Data replication strategies will most affect this metric, as the choice of strategy will determine how much recent data is available for recovery purposes.
RPO is measured in time.
The RTO indicates the amount of system downtime defining the total time of the disaster until the business can resume operations.
This is the goal for recovery of operational capability after an interruption in service (i.e., the amount of time it takes to recover). For example, a company might have an MAD of one week, while the company's BCDR plan includes and supports an RTO of six days.
RTO is measured in time. The RTO must be lower than the MAD.
The recovery service level is a percentage measurement (0-100%) of how much computing power is necessary based on the percentage of the production system needed during a disaster.
For example, an RSL of 50% would specify that the DR system would need to operate at a minimum of 50% the performance level of the normal production system.
RSL is measured in percentage.
Not to be confused with SSO or federated SSO, RSO refers to not having to sign into each piece of data or store once authorization has been granted. It generally operates through some form of credential synchronization. RSO introduces security issues not experienced by SSO because the nature of SSO eliminates usernames and other sensitive data from traversing the network.
The foundation of federation relies on the existence of an identity provider; therefore, RSO has no place in a federated identity system.
Deploying duplicate devices that can take over active operation if the primary device fails.
Re-running functional and non-functional tests to ensure that previously developed and tested software still performs after a change. If not, that would be called a regression.
A ROC is a form that has to be filled by all level 1 merchants undergoing a PCI DSS audit. The ROC form is used to verify that the merchant being audited is compliant with the PCI DSS standard.
Reputational risk is the loss of value of a brand or the ability of an organization to persuade.
A reservation creates a guaranteed minimum resource allocation that the host must meet.
The risk that exists after controls have been implemented.
The ability to restore normal operations after a disruptive event. Redundancy is the foundation of resiliency.
A term used to describe a profitability ratio.
Generally calculated by dividing net profit by net assets.
Risk appetite is the total risk that the organization can bear in a given risk profile, usually expressed in aggregate. Risk appetite is set by senior management and is the level, amount, or type of risk that the organization finds acceptable.
- Organizations accept a level of risk that allows operations to continue in a successful manner.
- It is legal and defensible to accept risks higher than the norm, or greater than your competitors, except risks to health and human safety; these risks must be addressed to the industry standard or whatever regulator motif to which your organization adheres.
As risk appetite or tolerance increases, so does the willingness to take greater and greater risks.
Risk modeling is based on an asset or a threat.
These are the individuals in the organization who together determine the organization's overall risk profile. For example, while one department may be willing to take moderately high risks in engaging cloud activities, another may have a lower risk tolerance. It is the aggregate of these individual tolerances that determines the organization's overall risk appetite.
The risk profile of the organization is a comprehensive analysis of the possible risks the organization is exposed to. It lists the identified risks and their potential effects.
The risk profile is determined by an organization's willingness to take risks as well as the threats to which it is exposed. The risk profile should identify the level of risk to be accepted, the way risks are taken, and the way risk-based decision making is performed. Additionally, the risk profile should take into account potential costs and disruptions should one or more risks be exploited.
A risk register is a table to consolidate information about risks.
Risk tolerance is the level of risk that an organization can accept per individual risk.
Identities can have multiple roles which indicate context. "Role" is a confusing and abused term used in many different ways. For our purposes we will think of it as similar to a persona, or as a subset of a persona. For example, a given developer on a given project may have different roles, such as "super-admin" and "dev", which are then used to make access decisions.
#
S
- Testing untested or untrusted code
- To better understand if an application is working the way it was intended to work
New computing resources can be assigned and allocated without any significant additional capital investment on the part of the cloud provider, and at an incremental cost to the cloud customer.
Scoping is the process that refers to including only departments or business units impacted by any (cloud) engagement.
When one risk response triggers another risk event. For example, a fire suppression system that displaces oxygen is a means to mitigate the original risk (fire) but adds a new risk (suffocating people).
The owner's right to determine to whom information is disclosed. Security protects privacy.
See
The PCI DSS SAQs are validation tools intended to assist merchants and service providers report the results of their PCI DSS self-assessment.
Examples include CVV or PIN numbers.
Dictates that one person/entity cannot complete an entire transaction alone.
In the case of encryption, a single entity should not be able to administer the issuing of keys, encrypt the data, and store the keys, because this could lead to a situation where that entity has the ability to access or take encrypted data.
Concerned more about the processing system rather than the data being replicated.
Views software as a combination of interoperable services, the components of which can be substituted at will.
Service levels indicate the minimum expected performance.
A method for automating account creation.
- Standardized
- Seldom implemented due to inflexibility and lack of vendor support
- Older and uses XML, which is slow
Performed by the customer organization to determine the importance of a particular patch or update.
Money spent on technology to acquire services without the IT department's dollars or knowledge.
For example, on-demand self service promotes and allows the ability to provision computing resources without human interaction, The consumer can provision resources regardless of location and time. This can be a challenge to purchasing departments as the typical purchasing processes can be avoided.
The concept of shares is used to arbitrate the issues associated with compute resource contention situations. Share values are used to prioritize compute resource access for all guests assigned a certain number of shares. Shares allow the cluster's reservations to be allocated and then addresses any remaining resources that may be available for use by members of the cluster through a prioritized percentage-based allocation mechanism.
The configuration when an enterprise deploys applications in dedicated infrastructure.
Having silos in an enterprise deployment could be a precursor to migrating the environments to the cloud.
Usage and administration of cloud services ought to be transparent to cloud customers and users; from their perspective, a digital data service is paid for and can be used, with very little additional input other than what is necessary to perform their duties.
The Smurf attack is a distributed denial-of-service attack in which large numbers of Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) packets with the intended victim's spoofed source IP are broadcast to a computer network using an IP broadcast address. Most devices on a network will, by default, respond to this by sending a reply to the source IP address. If the number of machines on the network that receive and respond to these packets is very large, the victim's computer will be flooded with traffic.
The action of grabbing data and using it without the owner's consent.
Encompasses the development and implementation of methods and processes for ensuring that software functions as intended while mitigating the risks of vulnerabilities, malicious code, or defects that could bring harm to the end user.
Automates security controls.
Performing an analysis of the source code, byte code, and binaries.
The term used to describe the destruction of potential evidence (intentionally or otherwise); in various jurisdictions, it can be a crime, or the grounds for another lawsuit.
A phenomenon that occurs when the number of VMs on a network reaches a point where the administrators can no longer manage them effectively.
Sprawl is a virtualization risk that occurs when the amount of content grows to such a degree that management is near impossible.
To prevent sprawl, the administrator should define and enforce a process for the deployment of VMs and create a library of standardized VM image files.
Step-up authentication is an additional factor or procedure that validates a user's identity by using the following means:
- Challenge questions
- Out-of-band authentication (phone call or SMS)
- Dynamic knowledge-based authentication (questions unique to the end user)
Works with a local service to store or archive data to secondary storage using a SAN. This would typically be in the same location.
SCIM is a standard for exchanging identity information between domains. It can be used for provisioning and deprovisioning accounts in external systems and for exchanging attribute information.
- Standardized
- Open standard for automating the exchange of user identity information between identity domains or IT systems
- Newer than SPML
#
T
Tenants, while running on the same host, are maintained separately in their virtual environments. This is known as tenancy separation.
Something that could cause loss to all or part of an asset.
Something or someone that carries out the attack. Also known as a threat agent.
Something or someone that carries out the attack. Also known as a threat actor.
When the server proves its identity to the client.
Top Threats is a working group established by the CSA that aims to provide organizations with an up-to-date, expert-informed understanding of cloud security risks, threats and vulnerabilities in order to make educated risk-management decisions regarding cloud adoption strategies.[[1]]
The risk that exists &before& any controls are implemented.
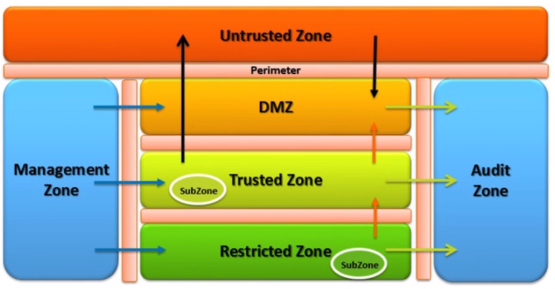
A trust zone is a network segment within which data flows relatively freely, whereas data flowing in and out of the trust zone is subject to stronger restrictions. These could be physical, logical, or virtual boundaries around network resources, such as:
- DMZ (semi-trusted)
- Department-specific zones/site-specific zones
- Application-defined zones (such as web application tiers)
Before a cloud provider can implement trust zones, they must undergo threat and vulnerability assessments to determine where their weaknesses are within the environment. This will help to determine where trust zones would be most helpful.
When controls implemented by the virtualization components are deemed to be not strong enough, trust zones can be used to segregate the physical infrastructure.
To protect trust zones:
- Implement granular role-based controls on traffic, users, and assets
- Manage inter-zone communications including between sub-zones
- Enforce policy and regulations
- Protect, detect, and contain
A physical chip on a host device which stores RSA encryption keys specific to that host for hardware authentication. The purpose is to provide WDE in the event that a hard drive is removed from its host.
The key difference between HSM and TPM is that an HSM manages keys for several devices, whereas a TPM is specific to a single device.
#
U
Underpinning contracts are external contracts negotiated between the organization and their vendors or suppliers.
#
V
Refers to the optimization of cloud computing and cloud services for a particular vertical (e.g., a specific industry) or specific-use application.
#
W
The Wassenaar Arrangement, formally established in July 1996, is a voluntary export control regime whose 42 members exchange information on transfers of conventional weapons and dual-use goods and technologies. This includes import restrictions and data sharing.
A WAF is a type of firewall that filters HTTP traffic and can help prevent DoS attacks.
A WAF operates at layer 7 of the OSI model.
A type of long-term storage, meaning it is written to initially and only used for read purposes thereafter.
Reviewing the source code.
A workaround is a temporary way of overcoming technical difficulties (such as incidents or problems).
The time necessary to very restoration of systems once they have been returned to operation.
#
X
XML gateways transform how services and sensitive data are exposed as APIs to developers, mobile users, and the cloud. They can be either hardware or software based and they can implement security controls such as DLP, antivirus, and antimalware. XML gateways can also act as a reverse proxy and perform content inspection on many traffic protocols, including SFTP.
#
Y
#
Z
#
Sources
- Gordon, A. (2016). The Official (ISC)² Guide to the CCSP CBK. Sybex.
- Malisow, B. (2017). CCSP (ISC)² Certified Cloud Security Professional Official Study Guide. Sybex.
- Carter, D. (2017). CCSP Certified Cloud Security Professional All-in-One Exam Guide. McGraw-Hill Education.
- Handerhan, K. (2019). Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP) [Video series]. Cybrary. https://www.cybrary.it/
- [VMware End-User Computing] (2019, June 7). Identity and Access Management: Technical Overview [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Tcvsefz5DmA
- [VMware End-User Computing] (2019, December 12). SAML 2.0: Technical Overview [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SvppXbpv-5k
- [OktaDev] (2019, November 5). An Illustrated Guide to OAuth and OpenID Connect [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t18YB3xDfXI
- [Programming with Mosh] (2018, January 19). What is a REST API? [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SLwpqD8n3d0
- Cloud Security Alliance. (2017). Security Guidance v4.0 [PDF file]. https://cloudsecurityalliance.org/research/guidance/
- Center for Internet Security. (2021, May 18). CIS Critical Security Controls Version 8 [PDF file]. https://www.cisecurity.org/controls/v8

